- Top
- Investor Relations
- Management Policy
- Corporate Governance
- Overview of Corporate Governance "Systems"
Overview of Corporate Governance "Systems"
Last update: July 10, 2025
Corporate Governance System (as of May 27, 2025) [CGC Supplementary Principle 4.10.1]
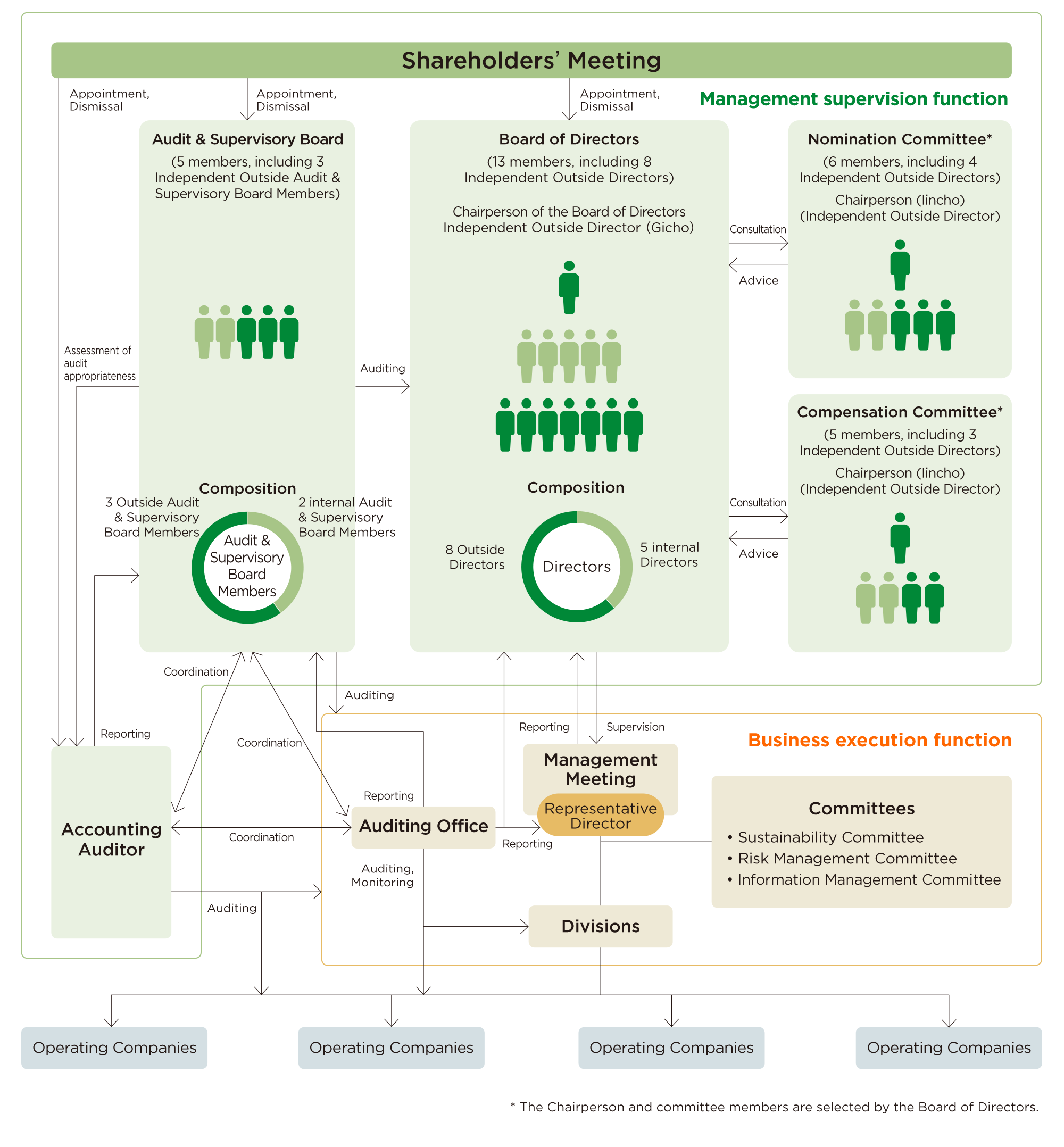
1. Reason for adoption of current corporate governance system
The Company ensures the effectiveness of its corporate governance by coordinating "audits"
conducted by the Audit & Supervisory Board Members (Audit & Supervisory Board), including multiple
Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members who maintain their independence and have specialized knowledge
in such areas as legal affairs and financial accounting, through their actively cooperating with the
accounting auditor and the internal audit division, and "formulation of management strategies" and
"supervision of business execution" conducted by the Board of Directors, including multiple Outside Directors
who maintain their independence and have advanced management knowledge and experience.
The Company has
adopted this corporate governance structure because it judges the structure to be workable for realizing and
ensuring the Company's corporate governance and for conducting appropriate and efficient corporate management.
Utilization of the company with Audit & Supervisory Board Member system
The Company considers the following characteristics and advantages of the Audit & Supervisory Board Member system to be effective for ensuring the appropriateness of the Company's Group governance and has therefore adopted it as the corporate governance system:
- 1Each Audit & Supervisory Board Member independently has its own auditing authority (individual independence system), which allows audits to be conducted from the perspectives of each Audit & Supervisory Board Member.
- 2The independence of the Audit & Supervisory Board Members is clearly specified by law, which enables independent and objective audits.
- 3The Audit & Supervisory Board Members have legally specified authority to investigate subsidiaries, which is effective also from a Group audit perspective.
Composition of Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board Members at each meeting body (as of June 23, 2025)
| Name | Position in the Company | Board of Directors | Audit & Supervisory Board | Nomination Committee | Compensation Committee | Management Meeting | Sustainability Committee | Risk Management Committee | Information Management Committee |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Junro Ito | Representative Director and Chair(Kaicho) Executive Officer and Chair(Kaicho) |
◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◎ | ◯ | ◯ | ||
| Stephen Hayes Dacus | Representative Director and President Executive Officer and President |
◯ | ◯ | ◎ | ◯ | ||||
| Shigeki Kimura | Representative Director and Vice President Executive Officer and Vice President |
◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◎ | ||
| Yoshimichi Maruyama | Director Managing Executive Officer |
◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | |||
| Tamaki Wakita | Director Managing Executive Officer |
◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◎ | ◯ | ||
| Fuminao Hachiuma | Independent Outside Director | ◎ | ◯ | ||||||
| Yoshiyuki Izawa | Independent Outside Director | ◯ | ◯ | ||||||
| Meyumi Yamada | Independent Outside Director | ◯ | ◎ | ◯ | |||||
| Paul Yonamine | Independent Outside Director | ◯ | ◎ | ||||||
| Takashi Sawada | Independent Outside Director | ◯ | |||||||
| Masaki Akita | Independent Outside Director | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | |||||
| Tatsuya Terazawa | Independent Outside Director | ◯ | |||||||
| Christine Edman | Independent Outside Director | ◯ | |||||||
| Shinya Ishii | Standing Audit & Supervisory Board Member | ◎ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | |||
| Nobutomo Teshima | Standing Audit & Supervisory Board Member | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | |||
| Kazuhiro Hara | Independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Member | ◯ | |||||||
| Mitsuko Inamasu | Independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Member | ◯ | |||||||
| Kaori Matsuhashi | Independent Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Member | ◯ |
2. Separation of the Board of Directors' supervisory functions and executive officers' business execution functions through introduction of the executive officer system (clarification of the scope of matters delegated to management)
To facilitate prompt decision making and business execution even amid a dramatically changing operating environment, the Company has introduced the executive officer system and separated the Board of Directors' supervisory functions from the executive officers' business execution functions. This developed an environment where the Board of Directors is able to focus on the "formulation of management strategies" and the "supervision of business execution," while the executive officers can focus on "business execution." The executive officers comprise 19members(16men and three women) as of June 23, 2025.
Clarification of the scope of matters delegated to
management
[CGCSupplementary Principle 4.1.1]
[CGCSupplementary Principle 4.1.1]
Matters to be decided by the Board of Directors at the Company are stipulated in the Board
of Directors Regulations, the Decision Authority Regulations, and so forth, and matters stipulated by the
Companies Act and the Company's internal regulations are decided by the Board of Directors.
The
Decision Authority Regulations clearly set forth the scope of matters to be decided by the Management
Meeting and the Representative Director and President. This clarifies the decision-making process for
management and the structure of responsibility, while also expediting decision-making by rational
delegation of authority.
3. Nomination Committee and Compensation Committee system [CGCPrinciple 3.1 (iii) (iv)][CGC Supplementary Principle 4.10.1][CGCSupplementary Principle 4.11.1]
(1) Outline of basic policy and system
The Company has established the “Nomination Committee” and the “Compensation Committee” (in this paragraph, “the Committees”) as advisory committees to the Board of Directors. The Committees' chair and the majority of their members are Independent Outside Directors. It has been utilizing the more diverse range of knowledge and advice of Outside Directors and Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members to ensure further objectivity and transparency in procedures for deciding the nomination of and compensation for Representative Directors, Directors, Audit & Supervisory Board Members, and executive officers (in this paragraph, “Officers, etc.”), thereby enhancing the supervisory functions of the Board of Directors and further substantiating corporate governance functions.
(Main items for deliberation by each committee and scope of target persons)
| Committee | Main items for deliberation | The Company | Core operating companies *1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | Overseas | ||||||||||
| Representative Director | Director | Audit & Supervisory Board Member | Executive Officer | Representative Director | Director | Audit & Supervisory Board Membe | Executive Officer | President, CEO | Position equivalent to President, CEO | ||
| Nomination Committee | Basic policies and standards for nomination of candidates | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ||||
| Contents of appointment proposals for candidates | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | |||||
| Compensation Committee*2 | Basic policies and standards for compensation, etc. | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ |
| Contents of proposals for the limit on the total amount of compensation, etc. | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | |||||
| Contents of individual compensation, etc. | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ◯ | ||||||
- *1As of May27,2025, “core operating companies” are SEVEN-ELEVEN JAPAN CO., LTD., Ito-Yokado Co., Ltd., York-Benimaru Co., Ltd., 7-Eleven, Inc., and 7-Eleven International LLC.
- *2In addition to the deliberation items above, the
Compensation Committee deliberates on important matters related to the establishment of the
stock-based compensation system, the establishment and change of stock grant criteria, and the
operation of stock-based compensation system (including decisions about updates) for Officers, etc. of
the Company and its domestic subsidiaries, and for Presidents, CEOs, and other similar positions of
overseas subsidiaries.
As of May27,2025, Audit & Supervisory Board Members are not subject to the stock-based compensation system.
(2) Proper Group management and utilization of the Nomination Committee and Compensation Committee
The Committees deliberate on the nomination and compensation of not only the Company’s
Officers, etc., but also Representative Directors of the core domestic operating companies and President and
CEO of the core overseas operating companies (in this paragraph, “Representative Directors, etc.”).
The
Representative Directors, etc., of the core operating companies occupy an important position for the Group's
management and are included within the purview of deliberations by the Committees from the perspective of
emphasizing the objectivity and transparency of the principal nomination and compensation procedures for the
management of not only the Company but also the Group.
The Company will also appropriately determine the
companies to be "core operating companies" with an emphasis on the objectivity and transparency of the Group
management procedures, in accordance with the Group's business portfolio strategy and governance system.
(3) Involvement of Audit & Supervisory Board Members from the perspective of ensuring correct procedures
Internal and outside Audit & Supervisory Board members act as observers on the
Committees.
They monitor the appropriateness of deliberation procedures and the reasonableness of
considerations related to each agenda item discussed by the two committees, which serve as advisory bodies
to the Board of Directors, from an objective standpoint. They also provide opinions from an impartial and
objective perspective to contribute to the Company’s sustainable growth and the enhancement of its medium-
to long-term corporate value.
4. Auditing
(1) Audits by the Audit & Supervisory Board Members
The Company's Audit & Supervisory Board develops audit plans with the basic audit policies
of ensuring sound and sustainable growth of the Company and its Group companies and establishing
high-quality corporate governance systems to respond to public trust. The Audit & Supervisory Board sets
the establishment of internal control systems, and the system to promote legal compliance and risk
management, as key audit items.
The Audit & Supervisory Board Members attend the Board of Directors
meetings and other important meetings. They conduct audits in the following manner: exchanging opinions with
the Representative Directors and periodically interviewing Directors and others on the status of business
execution; viewing important documents for approval such as request forms; and surveying the status of
operations and assets at the Head Office and others. For subsidiaries, they communicate and share
information with the Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board Members of subsidiaries, visit the
subsidiaries' Head Offices and stores to survey the actual status of operations in accordance with the audit
plans, and receive reports.
(2) Internal audits
We have established an Auditing Office as an independent internal audit department to evaluate the internal controls related to financial reporting for the entire Group.
In addition to auditing our own holding company, we conduct a confirmation of internal audits or direct audits of major operating companies, including the establishment and operation of compliance systems, in order to enhance and strengthen the audit functions of the entire group.
(As of April 30, 2025, there are 28 full-time internal audit staffs.)
Furthermore, the results of evaluations of internal controls related to financial reporting and the results of internal audits are reported to the Representative Director, relevant Officers, and the Board of Directors, and also reported to the Audit & Supervisory Board. We collaborate and consult with the Audit & Supervisory Board member audits to enhance the effectiveness of audits.
(3) Coordination between Audit & Supervisory Board member audits, internal audits, and accounting audits
(a) Coordination between the Audit & Supervisory Board members, the Auditing Office, and the accounting auditor
To improve the quality of audits across the Group, the Company ensures that the Audit & Supervisory Board members, the Auditing Office, and the accounting auditor proactively exchange information and opinions, and engage in discussions to maintain close ties with each other, by such means as periodically holding tri-partite meetings.
| Coordination method | Schedule | Proceedings |
|---|---|---|
| Tri-partite meetings | April, October | Exchanges information on the performance of accounting audits with the accounting auditor, the performance of internal audits with the Auditing Office, and the performance of Audit & Supervisory Board Member audits with the Audit & Supervisory Board Members and conducts exchanges of opinions. |
(b) Coordination between the Audit & Supervisory Board members and the accounting auditor
The Audit & Supervisory Board members receive reports from the accounting auditor at the beginning of the fiscal year on the annual audit plan, and on the procedures and results of accounting audits and internal control audits on a quarterly basis, and exchange opinions to coordinate with them..
| Coordination method | Schedule | Proceedings |
|---|---|---|
| Explanation of audit and midterm review plans | June | Receives an explanation of the audit plan and proposed audit fees for the fiscal year from the accounting auditor. |
| Report of midterm review (Status of annual audits) results | July, October, January | Receives reports on midterm review (Status of annual audits) results from the accounting auditor and exchanges opinions. |
| Interview with Audit & Supervisory Board members | January | Conducts interviews and exchanges opinions with the Audit & Supervisory Board members from the accounting auditor. |
| Exchange of opinions on key audit matters (KAM) | June, July, October, January, April |
Periodically receives explanations from the accounting auditor on matters that may become KAM and on the draft text thereof, and, upon reviewing the contents of those matters and texts, exchanges opinions. Considers the appropriateness of information disclosure |
| Report on audit results under the Companies Act | April | Receives a report on the audit results under the Companies Act from the accounting auditor. |
| Report on audit results under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act | May | Receives a report on the audit results under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act from the accounting auditor. |
| Report on the audit results of major overseas subsidiaries | August | Receives reports on audit results from the accounting auditor of affiliated firms overseas and exchanges opinions. |
| Accompanies on-site audits of Group companies | August, February | Accompanies on-site audits of Group companies by the accounting auditor to verify the appropriateness of audits. |
(c) Coordination between the Audit & Supervisory Board Members and the Auditing Office
The Audit & Supervisory Board Members and the Auditing Office ensure comprehensive sharing of audit information between each other in order to improve the quality of audits.
| Coordination method | Schedule | Proceedings |
|---|---|---|
| Regular meetings between the Standing Audit & Supervisory Board Members and the Auditing Office | Monthly | Receives reports from the Auditing Office on the audit plan, the results of operational audits, the progress of internal control evaluations, etc., and exchanges opinions. The Standing Audit & Supervisory Board Members report important matters to Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members. |
| Information sharing and exchange of opinions on the status and results of internal audits | June | Receives reports on the results of operational audits and activity status from the Auditing Office and exchanges opinions. |
| Report on the status and results of evaluations of internal controls regarding the financial reporting | Quarterly | Receives reports from the Auditing Office on the internal controls regarding the Group’s financial reporting as stipulated by the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act. |
(d) At each audit, the Audit & Supervisory Board Members, the Auditing Office, and the accounting auditor receive reports and materials, etc. from the internal control divisions, and request explanations as deemed necessary, and the internal control divisions cooperate in the appropriate performance of these audits.
5. Corporate governance by various committees
The Company has established the "Sustainability Committee," "Risk Management Committee," and "Information Management Committee," which report to the Representative Directors. Each committee determines Group policies in cooperation with the operating companies, and strengthens corporate governance by managing and supervising their dissemination and execution.
Sustainability Committee
The Company has established the Sustainability Committee based on Sustainability Basic Rules
for the purpose of promoting, administrating and supervising the Sustainability activities of the entire
Group through operating activities in order to contribute to solving social issues and aim for sustainable
growth for both society and the Group. The Company has also established five subcommittees under the
Sustainability Committee tasked with the examination and promotion of concrete measures to promote
operating activities that will contribute to solving material issues (Materiality) identified to address
the expectations and demands of stakeholders and realizing a more thorough compliance practice. Through
these subcommittees, the Company has carried out initiatives to find solutions to issues and implemented
preventive measures.
Under the Sustainability Committee, to resolve the material issues which should
be tackled by the Group, the Company tasks a subcommittee with handling each relevant issue: the
“Environment Subcommittee” with helping reduce environmental burdens, such as climate change and depletion
of resources; the “Supply Chain Subcommittee” with building a sound supply chain that takes human rights
and the environment into consideration and with improving quality and ensuring safety for merchandise and
services; the “Corporate Ethics and Culture Subcommittee” with ensuring thorough awareness and adoption of
the Corporate Creed and the Corporate Action Guidelines, building worker-friendly workplaces, promoting
advancement of diverse human resources and improving the labor environments; the “Compliance Subcommittee”
with strengthening compliance and internal controls; and the “Social Value Creation Subcommittee” with the
planning, proposal and operation of new businesses originating from addressing social issues through the
main business, by utilizing business characteristics and management resources. These subcommittees have
formulated and carried out measures to address such individual issues on a Group-wide basis.
Through
the activities of these subcommittees, we continue to promote business activities that further ensure
compliance and contribute to the resolution of the material issues (Materiality) related to stakeholders,
while aiming for sustainable development of both society and our Group from a sustainability perspective.
Risk Management Committee
In accordance with the basic rules for risk management, the Company and its Group companies
establish, streamline, and manage comprehensive risk management systems, centered on the Risk Management
Committee, in order to properly analyze, evaluate, and appropriately respond to risks associated with each
business, with consideration for changes in the management environment and risk factors.
The Risk
Management Committee receives reports from the departments in charge of risk management regarding the risk
management status of the Company. The committee comprehensively determine, assess, and analyze risks and
discuss measures, and determine the future direction going forward.
In recent years, in addition to changes in the Group's internal environment, the impact of various changes in the external environment on business operations, including rising geopolitical risks and environmental, social, and governance (ESG)-related risks, has grown significantly. To address these changes, the Company is committed to risk management that takes into account not only short-term risks but also medium- to long-term risks. Furthermore, we are enhancing the effectiveness of risk management across the Group by identifying high-priority risks based on factors such as importance and commonality, and clarifying the roles and responsibilities of the Company and its Group companies.
Information Management Committee
In accordance with the Information Control Regulations, the Company has carried out risk analysis, evaluation and measures regarding the information handling of all operations-related information that is learned, created or retained by officers and employees of the Group under the Information Management Committee, chaired by the information management supervisor.
Continuing on from the previous fiscal year, this fiscal year, the Company strived to strengthen its information collection and management structure. It strengthened its structure to timely and appropriately collect important information on its Group companies and to then deal with that information in cooperation with those companies. At the same time, the Company worked to strengthen its structure to centrally manage that information and to report it to management and related departments without omissions or delays.
Moreover, while complying with laws, regulations and guidelines concerning information security and personal information protection, the Company is strengthening its information security structure mainly by reviewing its information handling procedures, tightening its management of contractors, providing education and drill to its officers and conducting review of reporting channel for security incidents in response to increasingly sophisticated and complex cyberattacks. It is also further refining organizational, human, physical, and technical safety management measures.
Furthermore, in order to raise the awareness of “Rules against Insider Trading,” which are internal regulations, and to prevent insider trading, we conduct internal training on insider trading prevention for our group officers to ensure that important information is handled appropriately.
The Company will continue to deploy and provide guidance on those efforts within its Group companies through the Information Management Committee. At the same time, it will work to enhance governance in information management by supporting the autonomous and continuous promotion of these efforts in its Group companies, while monitoring and evaluating their progress.
6. Risk management
(1) Basic approach to risk management
The Company is taking steps to appropriately manage various risks based on effective methods with practical application in order to increase corporate value while ensuring the continuous development of the Group. In managing the Group's risks, the Company employs an integrated approach that quantitatively and qualitatively evaluates the risks in every business domain faced by each Group company, and implements measures that avoid, transfer, mitigate, and retain risks.
(2) Group risk management system and risk evaluation process
The Company and its Group companies have established governing bodies such as the Risk
Management Committee, with the departments that oversee the overall risk management of the respective
companies as the secretariat.
As a general rule, the Risk Management Committee meets once every six
months to receive reports on the risk management status of the respective companies from the departments
responsible for the management of risks, to comprehensively determine, assess, and analyze risks and discuss
measures, and to determine the future direction going forward.
In addition, various risks are comprehensively assessed primarily from the perspectives of significance, commonality, visibility, and efficiency, and are classified into four risk categories. Based on these risk categories, the roles and responsibilities of the Company and each of its group companies are clarified, and the entities responsible for each risk implement improvement activities to enhance the effectiveness of risk management across the entire group. For details on the PDCA and evaluation processes for risk management, please refer to the “Risk Factors” link below.
(3) Utilization of risk management indicators
In FY2020, the Company introduced shared Group risk indicators (Key Risk Indicators, “KRIs”) to enhance the effectiveness of the Group’s risk management.
KRIs are quantitative monitoring indicators that facilitate the early detection of the materialization or potential materialization of risks, as well as the reduction and minimization of any possible damage and its impact. A total of 90 KRIs have been set.
In operations, priority risks and their KRIs are identified from the perspectives of the Company and its Group companies. The Company coordinates with its Group companies to take measures before any major incidents occur, conducting assessments from a Groupwide cross-organizational perspective alongside respective self-assessments.
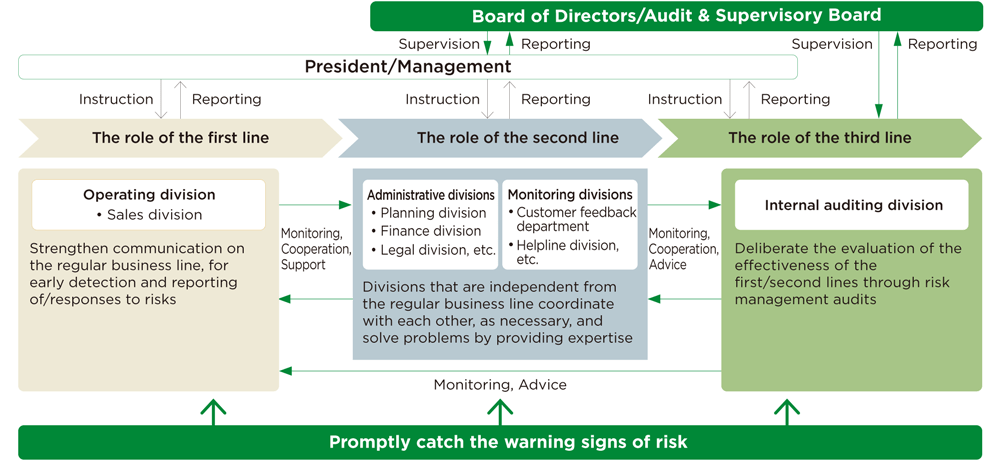
(4) To further strengthen risk management
As the business environment changes drastically, recognizing that prevention and early detection of incidents are crucial, the Company is promoting company-wide initiatives that require each line, i.e., the operating division-the first line, the administrative divisions- the second line, and the internal auditing division-the third line, to function properly.
In the first line, the operating division strengthens communication in the regular business line to ensure the early detection and reporting of/responses to risks onsite.
In the second line, the internal control promotion division, which is independent from the regular business lines (e.g., the administrative divisions and monitoring divisions), has established a system to give feedback, advice and support to the operating division, the first line, regarding the information gathered daily, while engaging in mutual coordination, as necessary.
In the third line, the internal auditing divisions of the Company and its Group companies conduct the risk management audits that analyze and evaluate whether the first and second lines of each company are functioning properly.
In addition to the above, given the lightning speed of changes in today's business environment, the Company is strengthening analysis of information on social media as well as the content of opinions from its customers and other parties, as part of its efforts to strengthen early understanding of the warning signs of risk.
Toward further strengthening of risk management: detecting the warning signs of
risk
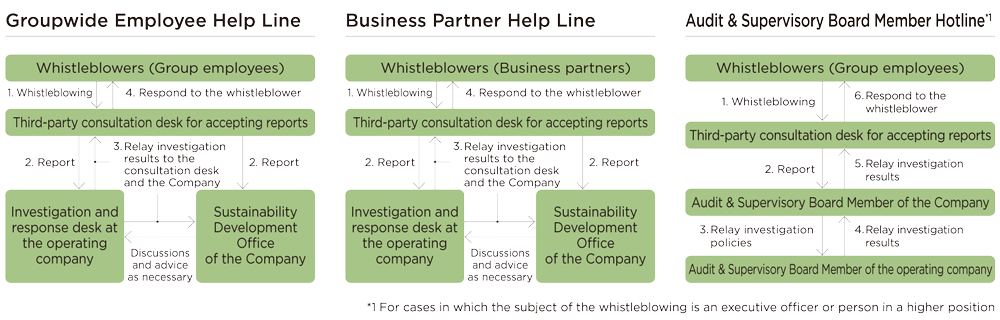
7. Internal whistleblowingUpdated
As part of the internal controls of the whole Group, the Group operates a "Groupwide Employee Help Line" for blowing the whistle by Group employees, a "Business Partner Help Line" for blowing the whistle by business partners, and an "Audit & Supervisory Board Member Hotline" regarding management team members, with the aim of preventing, rapidly identifying, rapidly rectifying, and preventing the recurrence of violations of laws and regulations, social norms, and internal rules.
- The Company has established a point of contact for reporting at an outside third-party organization to thoroughly protect those who issue reports by enabling reports to be made anonymously, ensuring the confidentiality of report content, protecting the personal information and privacy of the reporting person (whistleblower), and preventing the whistleblower from being subjected to disadvantageous treatment for having used the help line.
- When a serious violation is found to have occurred, it is reported immediately to a Representative Director. The relevant department and relevant companies then confer about the response and take necessary measures.
- The executive officer in charge of the secretariat of the Sustainability Committee at the Company regularly reports and confirms the operational status of the internal whistleblowing system at the Board of Directors' meeting.
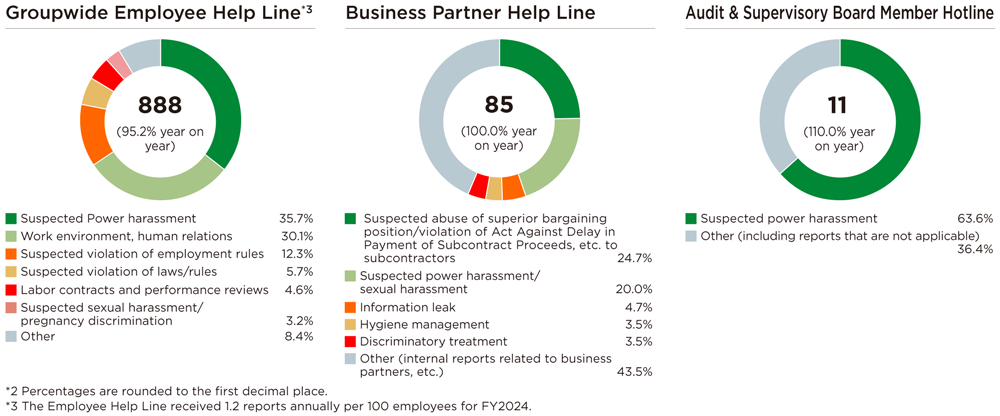
[Number of reports for FY2024]*2
8. Cross-shareholdings [CGCPrinciple 1.4]
(1) Policy on cross-shareholdings
Overall, the Group's cross-shareholdings as of the end of February 2025 comprise 42 stocks, with a market value of ¥95.4 billion accounting for 2.3% of consolidated net assets.
In principle, the Group does not hold cross-shareholdings except where there is an accepted rational for doing so, such as maintaining or strengthening business alliances or business relationships, in order to maintain and strengthen business competitiveness.
Stocks held are reviewed annually and shares with less rationale or less effectiveness for holding are to be sold in view of the circumstances of the investee companies.
- *The market value is rounded down to the nearest 10 million yen and the ratio is rounded to the first decimal place.
(2) Standards for exercising voting rights
When exercising voting rights as to listed cross-shareholdings, based on the following Detailed Rules regarding Standards for Exercising Voting Rights, the Company decides whether to vote for or against proposals from the perspective of increasing the medium- to long-term corporate value of the Company and the investee companies, and engages in dialogue with the investee companies about the proposals before exercising its voting rights if necessary.
Detailed Rules regarding Standards for Exercising Voting Rights
a. Whether proposals at each Shareholders' Meeting inure to medium-to long-term improvement of corporate value?
b. Whether proposals at each Shareholders' Meeting will maximize the benefits of shareholders of the company that convenes the Shareholders' Meeting?
c. Whether a convocation notice of Shareholders' Meetings and other materials such as documents that explain proposals are timely and appropriate as information disclosure?
(3) Determination of the rationale and effectiveness of shareholding
At the Board of Directors held on April 17, 2025, we reviewed the appropriateness of holding individual stocks based on quantitative criteria and the rationale of holding them in light of our relationships with business partners.
As a result, we will consider selling stocks for which the rationale for holding them has weakened, taking into account the impact on the stock market and other factors.
In addition, the Board of Directors has confirmed that group operating companies, excluding listed subsidiary, are also conducting reviews of listed cross-shareholdings in accordance with the same holding policy as the Company.
Matters reviewed
- Qualitative Matters
-
1. Background of acquisition
2. Presence or absence of business relationship
3. Strategic significance at the time of holding
4. Possibility of future business
5. Risks related to survival or stability, etc. of business if shares are not held
6. Continuity of advantages, future outlook for business, and risks if shares continue to be held
- Quantitative Matters
-
1. The most recent amounts of transactions and profits if any business is conducted through business alliances, etc.
2. Annual dividends received and gain or loss on valuation of shares
3. Whether the benefits and risks from each holding cover the Company's cost of capital
9. Advisors, etc. (as of May 27, 2025)
Status of the advisors,etc. for the Company and major companies is as below.
The Company
| Name | Toshifumi Suzuki |
|---|---|
| Title/position | Honorary Advisor |
| Duties | Provide advice when needed by the Company's management team |
| Working arrangement/conditions | Full-time/with compensation |
| Date of retirement of the Company's president, and representative director, etc. | May 26, 2016 |
| Term of office | 1 year |
| Name | Katsuhiro Goto |
|---|---|
| Title/position | Advisor |
| Duties | Provide advice when needed by the Company's management team |
| Working arrangement/conditions | Full-time/with compensation |
| Date of retirement of the Company's president, and representative director, etc. | May 28, 2024 |
| Term of office | 1 year |
| Name | Ryuichi Isaka |
|---|---|
| Title/position | Senior Advisor |
| Duties | Provide advice when needed by the Company's management team |
| Working arrangement/conditions | Full-time/with compensation |
| Date of retirement of the Company's president, and representative director, etc. | May 27, 2025 |
| Term of office | 1 year |
- Regarding the assumption of office by advisors of the Company and major operating companies, the Company's Board of Directors deliberates and confirms matters and appropriately supervises their work.
- Upon consultation from the Company's Board of Directors, the Company's Nomination Committee deliberates and confirms the duties, work arrangements, and conditions, such as compensation terms for the advisors of the Company and major operating companies.
- The roles of advisors of the Company and major operating companies are to provide advice when needed by the management team of each company, and advisors have no authority to affect the management decisions of each company.
10. Framework for checking related party transactions [CGC Principle 1.7]
With regard to transactions with related parties, the Company investigates and identifies
related parties and checks if there are any transactions with related parties and the details thereof. The
Company discloses the transactions in accordance with the Companies Act, the Financial Instruments and
Exchange Act, and other applicable laws and regulations, as well as the regulation of the Tokyo Stock
Exchange.
Furthermore, with regard to any competing transactions and conflict-of-interest transactions
between the Company and any Directors, the Company makes it a rule for the Directors to obtain approval of the
Board of Directors in accordance with laws and regulations and the Board of Directors Regulations and to
report material facts if the Directors carry out such transactions.
